ROX-Trike
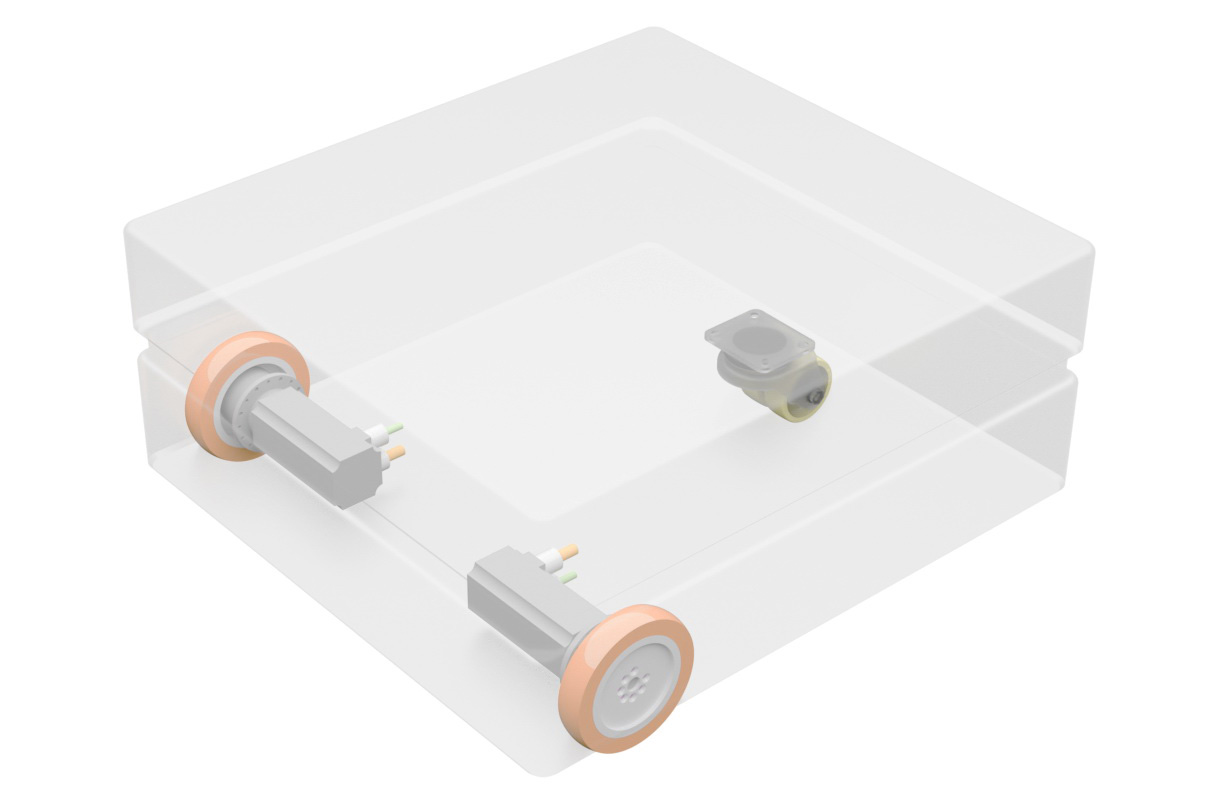
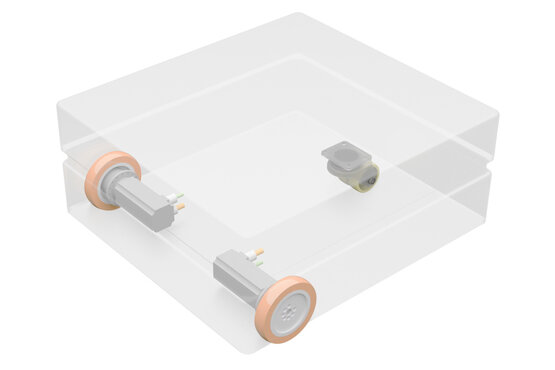
ROX Platform With Front Differential Drive
The front differential drive is the mechanically simplest and probably most commonly used differential kinematics after the central drive. It consists of two individually controlled drive wheels mounted without suspension in the two front corners of the platform, which carry most of the load. One or two passive castors at the rear of the robot complete the drive. The ROX-Trike usually consists of two swivel castors that guarantee stability while carrying heavy loads, making it suitable for industrial applications. Using only one castor can be justified when the surface is highly irregular, ensuring that the contact with the ground is consistent.
This configuration offers several advantages:
- The ROX-Trike offers a cost-effective solution compared to other available kinematics.
- The robot maintains exceptional stability and consistent ground contact, particularly when stationary. The platform is thus ideal for operations involving large lateral forces, such as high-speed robot arm motions.
On the other hand, there are some limitations:
- The robot requires a significantly larger turning radius than compared to the ROX-Diff. As a result, it is not ideally suited for very tight spaces.
- The asymmetrical design results in a clear preferred driving direction. Maneuvering and approaching targets require a bit more planning.
ROX-Trike
Basic configuration
Description
Turnkey system: 2x motors, 1x Sick S300 expert scanner, sealed lead battery 24V/50Ah, wireless joystick, manual charger, on-board computer (Intel i5, 8 GB RAM, >200 GB SSD, WLAN), ROS, documentation, CE conformity declaration
1 day training
Description
In Heilbronn for up to 3 persons
inclusive catering
inclusive catering
Basic support
Description
3 month support (Telefon/E-Mail)
Automatic charging station
i7 on-board computer
Description
Intel Core i7, 16 GB RAM, 400+ GB SSD
IOBoard
Second laser scanner
Description
Extended support
Description
Additional 6 months support
by telephone/e-mail/update
by telephone/e-mail/update